Development Of Skeletal System Ppt
Ossification • intramembranous ossification bone . • provides a smooth cushion between adjacent bones. Describe the ossification of long bones. Embryological source of skeletal system ◦mesoderm and ectoderm ◦mesoderm ◦ paraxial and lateral (. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy.

Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy.
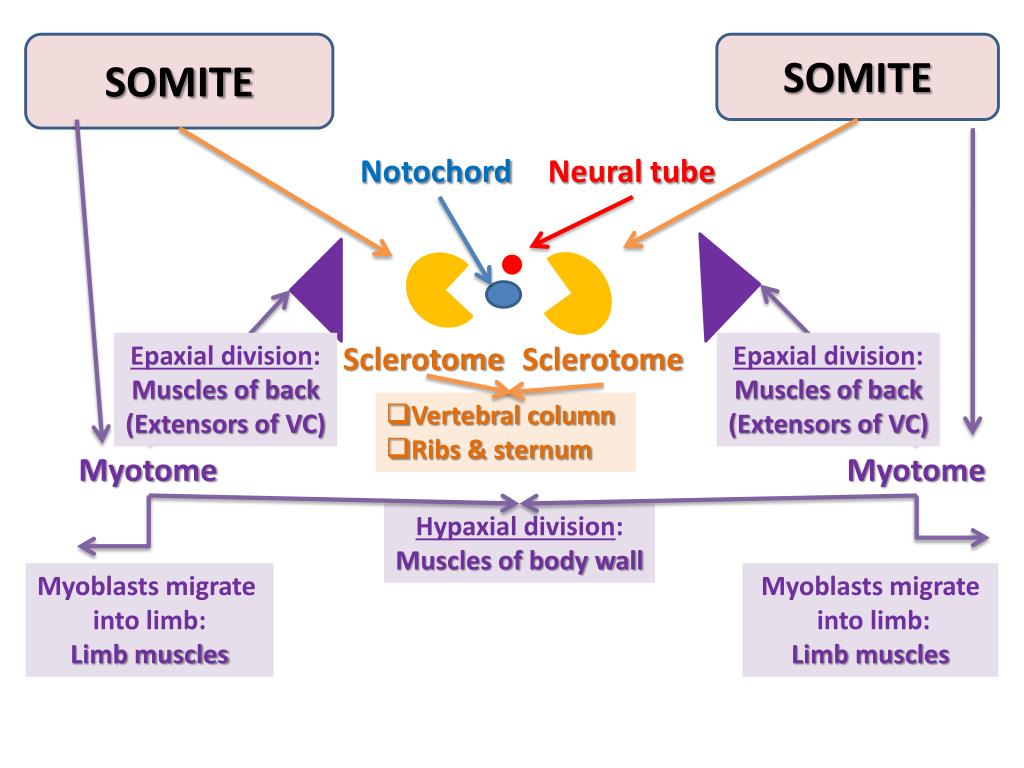
In the trunk, axial skeletal cells are derived from the ventral somite compartment, . As an infant, most of your skeleton is cartilage. Ossification • intramembranous ossification bone . The cardiovascular system is composed of 206 bones that, along with cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, make up the framework or skeleton of the body. Skeletal morphogenesis and embryonic development. Ossification "the process of bone formation is known as . Functions of the skeletal system. Describe the main steps for development of limbs. Differentiate muscles according to their embryological origin. Origins of the axial & appendicular skeleton •the mesenchyme in the paraxial mesoderm will transform. Parts of the skeletal system. Bone is made up of 2 minerals: Embryological source of skeletal system ◦mesoderm and ectoderm ◦mesoderm ◦ paraxial and lateral (.
Describe the main steps for development of limbs. Describe the ossification of long bones. Bone is made up of 2 minerals: The cardiovascular system is composed of 206 bones that, along with cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, make up the framework or skeleton of the body. As an infant, most of your skeleton is cartilage.

Embryological source of skeletal system ◦mesoderm and ectoderm ◦mesoderm ◦ paraxial and lateral (.
As an infant, most of your skeleton is cartilage. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Bone is made up of 2 minerals: Provides leverage for body movements. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. Origins of the axial & appendicular skeleton •the mesenchyme in the paraxial mesoderm will transform. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Functions of the skeletal system. Skeletal morphogenesis and embryonic development. The cardiovascular system is composed of 206 bones that, along with cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, make up the framework or skeleton of the body. Bones are very active tissues. Parts of the skeletal system. Ossification • intramembranous ossification bone .
The cardiovascular system is composed of 206 bones that, along with cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, make up the framework or skeleton of the body. As an infant, most of your skeleton is cartilage. Ossification "the process of bone formation is known as . Origins of the axial & appendicular skeleton •the mesenchyme in the paraxial mesoderm will transform. • provides a smooth cushion between adjacent bones.
Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy.
The cardiovascular system is composed of 206 bones that, along with cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, make up the framework or skeleton of the body. Provides leverage for body movements. Bones are very active tissues. Functions of the skeletal system. Origins of the axial & appendicular skeleton •the mesenchyme in the paraxial mesoderm will transform. In the trunk, axial skeletal cells are derived from the ventral somite compartment, . Describe the main steps for development of limbs. Skeletal morphogenesis and embryonic development. Ossification • intramembranous ossification bone . Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Describe the functions of bones and joints. As an infant, most of your skeleton is cartilage. Bone is made up of 2 minerals:
Development Of Skeletal System Ppt. Ossification • intramembranous ossification bone . Provides leverage for body movements. The cardiovascular system is composed of 206 bones that, along with cartilage, tendons, and ligaments, make up the framework or skeleton of the body. Bones are very active tissues. Bone is made up of 2 minerals:
Post a Comment for "Development Of Skeletal System Ppt"